Introduction & Overview of Javascript
Javascript is a high-level, interpreted programming language that is widely used for creating dynamic and interactive web pages.
Key Points:
- Client-side Language: Javascript runs on the client side, i.e., on the user’s browser, allowing dynamic changes without page reloads.
- Event-Driven: It is event-driven, responding to user actions such as clicks, scrolls, etc.
- Popular Libraries and Frameworks: Javascript has popular libraries and frameworks like jQuery, React, Angular, and Vue.js for front-end development.

Core Concepts & Terminology of Javascript
Variables
Variables are used to store data values.
Functions
Functions are blocks of code that can be defined once and executed any number of times.
Conditional Statements
Conditional statements allow you to make decisions in your code based on specified conditions.
Loops
Loops are used to repeatedly run a block of code a certain number of times or as long as a specified condition is met.
Arrays
Arrays are used to store multiple values in a single variable.
Objects
Objects are complex data types used to store collections of related data and more complex entities.

Architecture & How It Works of Javascript
Javascript runs on a single thread and uses an event loop for asynchronous operations. It consists of three main components:
- Engine: Parses and executes the code.
- Call Stack: Keeps track of function calls.
- Callback Queue: Stores callback functions to be executed.
When a script is executed, it goes through the following phases:
- Parse: The code is parsed into executable code.
- Execute: The code is executed line by line.
- Run-time: Variables are allocated memory and functions are called.

Installation & Getting Started
Follow the steps below to install and get started with JavaScript:
Install JavaScript
To start using JavaScript, you can include the following script tag in your HTML file:
<script src="path/to/your/javascript.js"></script>
Getting Started
To begin coding in JavaScript, you just need a text editor and a web browser. Write your JavaScript code in a .js file and link it to your HTML file using the script tag as shown above.
Happy coding!

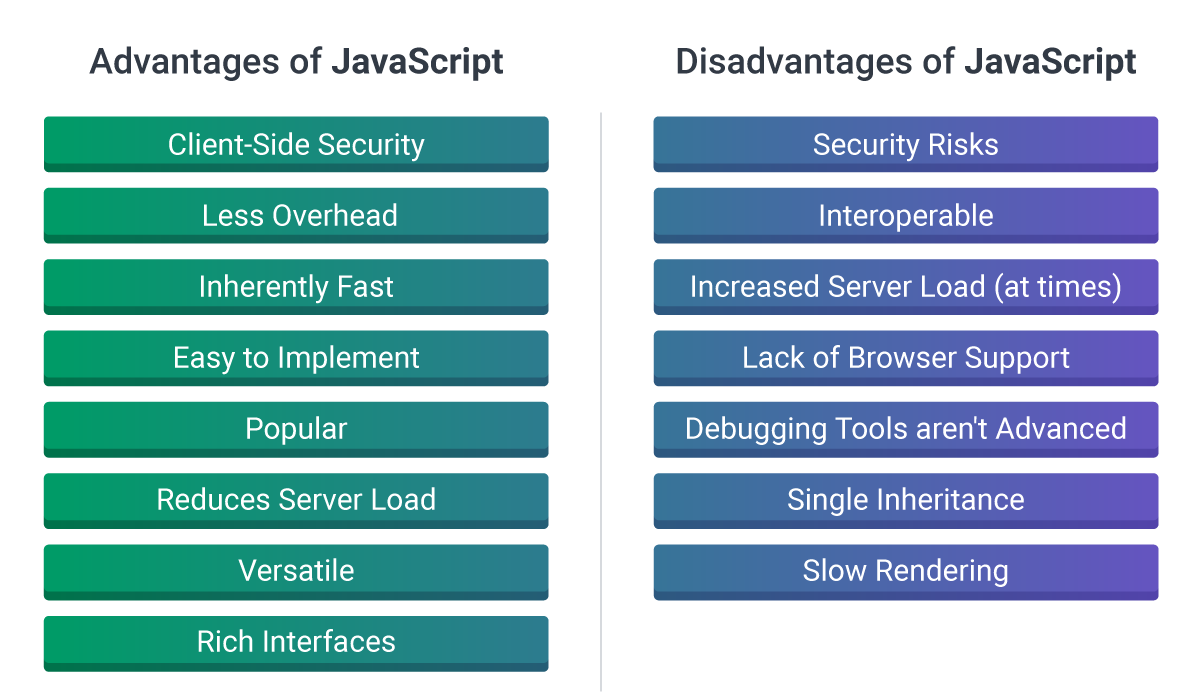
Benefits & Limitations of Javascript
Javascript is a versatile and powerful programming language that is widely used for web development. It offers several benefits, but also comes with its own set of limitations.
Benefits
- Client-Side Interactivity: Enables interactive and dynamic user interfaces.
- Wide Adoption: Supported by all major browsers, making it a popular choice for web development.
- Open Source: JavaScript frameworks and libraries are freely available for developers to use and customize.
Limitations
- Browser Support: Although widely supported, there can still be inconsistencies across different browsers.
- Security: Being executed on the client-side, Javascript can be vulnerable to attacks like cross-site scripting (XSS).
- Performance: Intensive operations can slow down the execution of Javascript, affecting user experience.
Real-World Use Cases of Javascript
Javascript is a versatile programming language that is extensively used in various real-world scenarios due to its adaptability and functionality.
Key Use Cases:
- Web Development: Javascript is a fundamental language for building interactive and dynamic websites.
- Mobile App Development: Frameworks like React Native and Ionic utilize Javascript for cross-platform app development.
- Game Development: WebGL and libraries like Phaser enable the creation of browser-based games using Javascript.
- Server-Side Development: Node.js allows developers to use Javascript for server-side programming.
- Data Visualization: Libraries like D3.js enable the creation of interactive data visualizations on the web.

Best Practices & Recommendations of Javascript
1. Maintain Code Consistency
Consistency in naming conventions, formatting, and coding style helps improve code readability and maintainability.
2. Use Modern ECMAScript Features
Stay up-to-date with the latest ECMAScript standards to leverage new features and improvements in JavaScript.
3. Avoid Global Variables
Avoid polluting the global namespace by minimizing the use of global variables and instead encapsulate code within functions or modules.
4. Optimize Loops and Iterations
When working with loops, try to optimize them for performance to prevent unnecessary bottlenecks in your code.
5. Implement Error Handling
Proper error handling using try…catch blocks can help in diagnosing and fixing issues in your JavaScript applications.
6. Test Code Thoroughly
Testing code through unit tests, integration tests, and end-to-end tests helps ensure the reliability and functionality of your JavaScript applications.

Comparison with Alternatives of Javascript
When comparing JavaScript with other alternatives, it is important to consider various factors such as performance, syntax, community support, and ecosystem.
Performance
JavaScript is a lightweight, interpreted language that runs on the client side, making it ideal for web development. However, when compared to compiled languages like C++ or Java, JavaScript may have performance limitations.
Syntax
JavaScript has a forgiving syntax that allows developers to write code quickly and with less boilerplate compared to languages like Java or C#. However, this flexibility can sometimes lead to unexpected behavior if not used carefully.
Community Support
JavaScript has a large and active community of developers who contribute libraries, frameworks, and tools to the ecosystem. This ensures that developers have access to a wide range of resources to help them build robust applications.
Ecosystem
The JavaScript ecosystem is vast and diverse, with a wide range of libraries and frameworks available for different use cases. From front-end frameworks like React and Angular to back-end frameworks like Node.js, JavaScript offers a versatile ecosystem for building applications.
