What is the main purpose of react?
React is a JavaScript library for building interactive user interfaces.
Key features of React:
- Component-based: UI divided into reusable components
- Virtual DOM: Efficiently updates and renders components
- JSX: Syntax extension for JavaScript to write HTML
- Unidirectional data flow: Data flows in one direction
Why should you consider using react?
There are several reasons why using React can be beneficial:
- Efficient DOM manipulation: React’s virtual DOM efficiently updates the real DOM, leading to faster rendering times.
- Component-based architecture: React promotes building reusable and modular components, making code more organized and easier to maintain.
- Virtual DOM: React’s use of a virtual DOM allows for fast and efficient updates to the UI without directly manipulating the entire DOM tree.
- JSX: JSX syntax allows for writing HTML-like code directly in JavaScript, making it more intuitive for developers to work with.

What are the key features offered by React?
React offers a range of key features that make it a popular choice among developers:
Virtual DOM
The virtual DOM enables efficient updates to the browser DOM, resulting in improved performance.
Component-Based Architecture
React follows a component-based structure, making it easier to manage and reuse code.
One-Way Data Binding
React implements one-way data flow, ensuring predictable data interactions and reducing bugs.
JSX Syntax
JSX allows developers to write HTML-like code within JavaScript, blending markup and logic.
React Hooks
Hooks provide a way to use state and lifecycle features in functional components, enhancing code organization.
Community Support
React has a vast and active community that contributes libraries, tools, and resources to support developers.

Who are the primary users of react?
React is primarily used by:
- Front-end Developers: React is a popular choice for building user interfaces in web applications.
- UI/UX Designers: Working closely with developers to create interactive and visually appealing designs using React components.
- Full-stack Developers: Integrating React into both front-end and back-end services to build scalable applications.
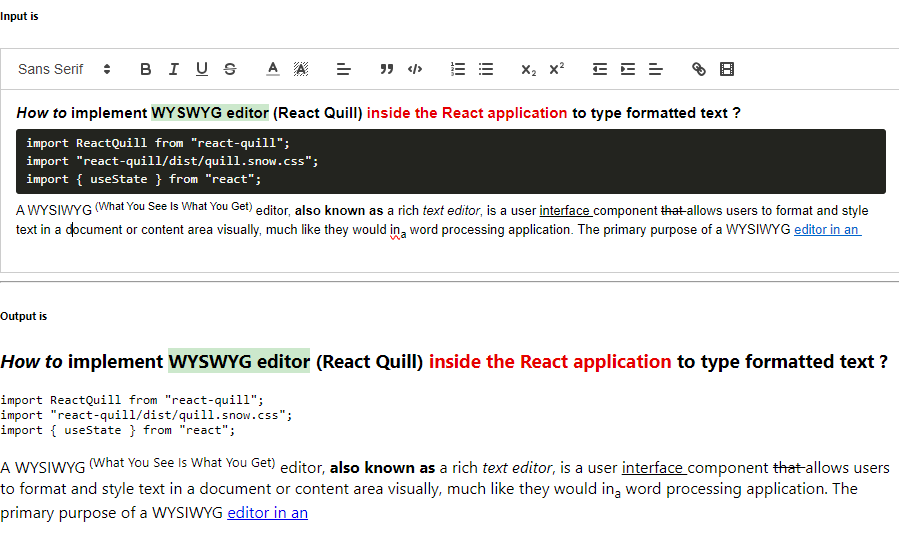
What are the typical use cases for React?
React is a popular JavaScript library used for building dynamic user interfaces. It is commonly used in the following scenarios:
- Single Page Applications (SPAs): React is well-suited for creating SPAs that provide a seamless user experience by updating content dynamically without reloading the page.
- Reusable UI Components: React’s component-based architecture allows developers to create reusable components, making it easier to maintain and update the UI of web applications.
- Complex Web Applications: React is suitable for building large and complex web applications that require a high level of interactivity and state management.
- Mobile App Development: React Native, a framework based on React, enables developers to build mobile applications for iOS and Android using JavaScript and React principles.
.png)
How do you get started with React?
Getting started with React is easy and straightforward. Here is a simple guide to help you kickstart your React journey:
1. Set up your development environment
Make sure you have Node.js installed on your machine. You can create a new React project using Create React App, which sets up your development environment with just a single command.
2. Learn the basics
Start by understanding the fundamental concepts of React, such as components, props, state, and lifecycle methods. There are plenty of resources available online to help you learn these concepts.
3. Build your first React application
Put your knowledge into practice by building a simple React application. Start with a small project to get a hands-on experience of working with React components and data flow.
4. Explore advanced topics
Once you are comfortable with the basics, delve into more advanced topics like Redux for state management, React Router for navigation, and integrating with backend APIs.
5. Join the React community
Connect with other React developers through forums, meetups, and online communities. Learning from others and sharing your experiences can accelerate your growth as a React developer.
How does it work, in the context of react?
React works by creating a virtual DOM that sits between the actual DOM and the React components.
Key Concepts:
- Components: Building blocks of a react application.
- Virtual DOM: Lightweight copy of the actual DOM for performance optimization.
- Reconciliation: Process of updating the actual DOM based on changes in the virtual DOM.
When a React component’s state or props change, React uses a process called reconciliation to efficiently update the actual DOM.

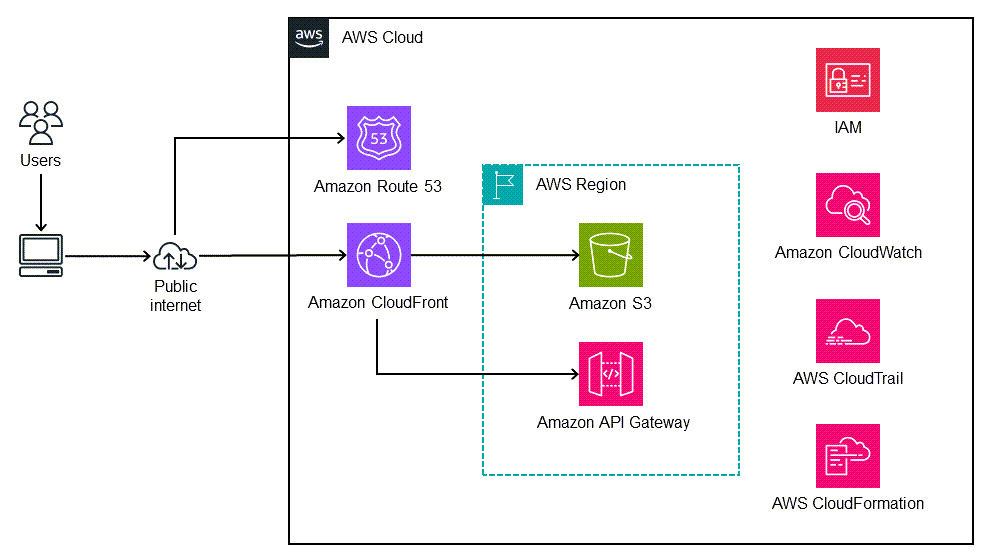
Where can you deploy or implement react?
There are various platforms where you can deploy or implement your React applications. Some of the popular options include:
- Web Hosting Services: Deploy your React app on platforms like Netlify, Vercel, GitHub Pages, or Firebase Hosting.
- Cloud Platforms: Use cloud services such as AWS, Google Cloud Platform, or Microsoft Azure to host your React applications.
- Containerization: Deploy your React apps as Docker containers and manage them with platforms like Kubernetes.
Comparisons of Other tools with react?
When comparing React with other frontend frameworks and libraries, there are several factors to consider:
Angular
Angular is a comprehensive framework developed by Google, which provides a more structured approach compared to React. It has a steep learning curve but comes with powerful features such as two-way data binding and dependency injection.
Vue
Vue is a progressive framework that shares some similarities with React. It is known for its simplicity and ease of integration with existing projects. Vue provides clear and concise documentation, making it an attractive choice for developers.
jQuery
jQuery is a lightweight library that simplifies DOM manipulation and event handling. Unlike React, which is a full-fledged library for building user interfaces, jQuery focuses on enhancing interactions with the DOM. However, jQuery lacks the component-based architecture that React offers.
