What is the main purpose of GitLab?
GitLab is a web-based DevOps lifecycle tool that provides a Git repository manager providing wiki, issue-tracking, and continuous integration/continuous deployment pipeline features, using an open-source license.
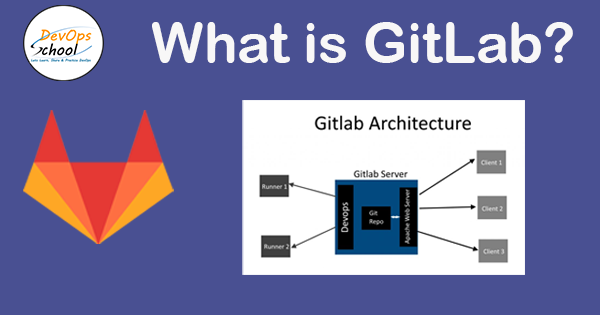
Why should you consider using GitLab?
There are several reasons to consider using GitLab:
1. Integrated Development Environment
GitLab provides a powerful integrated development environment that allows developers to manage their code, collaborate with team members, and streamline the development process.
2. Collaboration and Code Review
GitLab offers robust collaboration features such as merge requests, code reviews, and issue tracking, making it easier for teams to work together and maintain code quality.
3. Continuous Integration and Deployment
With GitLab’s built-in CI/CD pipelines, you can automate testing, building, and deploying your applications, helping you deliver high-quality code faster and more efficiently.
4. Scalability and Flexibility
GitLab is designed to scale with your growing development needs, whether you are a small team or a large enterprise. Its flexible infrastructure allows you to adapt and customize your workflows to suit your requirements.

What are the key features offered by gitlab?
GitLab provides a wide range of powerful features for managing your repositories and enabling collaboration. Some of the key features include:
1. Version Control
GitLab offers robust version control capabilities, allowing you to track changes, collaborate with teammates, and manage your codebase efficiently.
2. Issue Tracking
With GitLab’s built-in issue tracking system, you can easily create, assign, and organize tasks and issues within your projects.
3. Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
GitLab includes CI/CD pipelines that enable you to automate testing and deployment processes, ensuring a smooth and efficient release cycle.
4. Merge Requests
Collaborate effectively by using GitLab’s merge request feature, which allows team members to review, comment, and merge code changes seamlessly.
5. Wiki and Documentation
Create and maintain project documentation with GitLab’s Wiki feature, making it easy to keep important information up-to-date and accessible.
6. Code Review
Facilitate code reviews and ensure code quality with GitLab’s code review tools, which provide features such as inline comments and diffs.
Who are the primary users of GitLab?
GitLab is a versatile platform that caters to various categories of users, including:
- Developers who collaborate on coding projects
- DevOps teams responsible for continuous integration and deployment
- System administrators managing GitLab instances
- Project managers overseeing development workflows
What are the typical use cases for GitLab?
GitLab offers a wide range of use cases, catering to various needs of software development teams. Some common typical use cases include:
- Version Control and Source Code Management
- Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
- Issue Tracking and Project Management
- Collaboration and Code Review

How do you get started with GitLab?
Getting started with GitLab is easy and straightforward. Follow these steps:
1. Create a GitLab Account
If you don’t already have a GitLab account, you can sign up for a free account on the GitLab website.
2. Create a New Project
Once you have your GitLab account, you can create a new project by clicking on the “New Project” button on your dashboard.
3. Start Using GitLab
Now that you have set up your account and created a project, you can start using GitLab for version control, collaboration, and more.

How does it work, in the context of gitlab?
In the context of GitLab, the workflow typically involves the following steps:
- Version control: GitLab provides version control capabilities using Git, allowing teams to collaborate on code changes.
- Repository management: GitLab offers a centralized location for storing code repositories, enabling easy access and sharing.
- Issue tracking: Teams can utilize GitLab’s issue tracking system to manage tasks, bugs, and feature requests efficiently.
- Continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD): GitLab integrates CI/CD pipelines to automate the build, test, and deployment processes.
- Code review: GitLab facilitates code reviews by providing tools for commenting, suggesting changes, and approving merge requests.

Where can you deploy or implement gitlab?
GitLab can be deployed or implemented in various environments. Below are some common deployment options:
1. Self-Managed Servers
Self-managed servers provide full control over your GitLab instance and infrastructure. You can install GitLab on your own hardware or virtual machines.
2. Cloud Providers
Cloud providers like AWS, Google Cloud Platform, and Azure offer options to deploy GitLab on their infrastructure, allowing for scalability and ease of management.
3. GitLab.com
GitLab.com is the official SaaS (Software as a Service) offering by GitLab, where you can sign up for a hosted version of GitLab without needing to manage the infrastructure.
Choose the deployment option that best fits your needs and resources.

What are the limitations or challenges associated with gitlab?
GitLab, like any other software, has its share of limitations and challenges. Some of these include:
1. Scalability:
GitLab may face challenges with scalability when managing large projects or repositories with a high number of files and users.
2. Customization Complexity:
Customizing GitLab to meet specific requirements can be complex and may require significant expertise.
3. Resource Intensive:
Running GitLab can be resource-intensive, especially in terms of memory and processing power.
4. Learning Curve:
GitLab has a learning curve, and users may require time to fully understand its features and functionalities.
5. Dependency on Internet Connectivity:
GitLab’s functionality is closely tied to internet connectivity, which can be a limitation in offline or low-bandwidth environments.

Comparisons of Other tools with gitlab?
When comparing GitLab with other tools, it is important to consider the following aspects:
Features
- GitLab offers a comprehensive set of features for version control, project management, CI/CD, and more.
- Other tools may have a different focus or offer a subset of the features provided by GitLab.
Integration
- GitLab provides seamless integration with various third-party tools and services.
- Other tools may have limitations in terms of integration options and compatibility.
Overall, GitLab stands out as a powerful all-in-one solution for development teams looking to streamline their workflows and collaboration.
