What is the main purpose of NPM?
NPM, which stands for Node Package Manager, is a package manager for the JavaScript programming language. Its primary purpose is to help developers manage dependencies and packages efficiently in their projects.
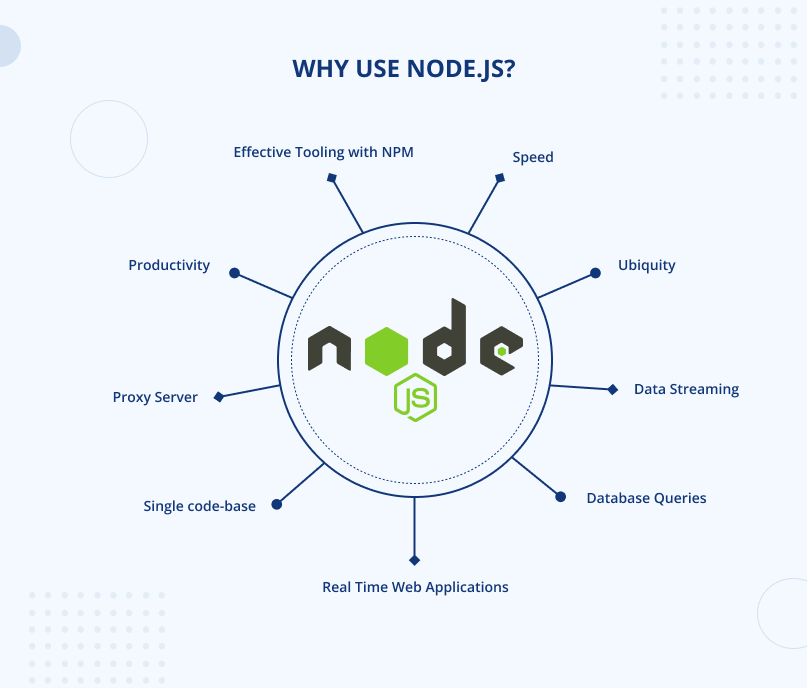
Why should you consider using NPM?
NPM (Node Package Manager) is a powerful tool that offers several benefits for developers:
- Large Package Ecosystem: NPM provides access to a vast array of reusable code packages for development projects.
- Package Version Management: NPM allows developers to easily manage and update package versions to ensure project stability.
- Dependency Management: NPM handles dependencies between packages, making it easier to manage project requirements.
- Command-line Interface: NPM offers a user-friendly command-line interface for installing, updating, and removing packages.

What are the key features offered by NPM?
NPM (Node Package Manager) offers a variety of features for managing packages and dependencies within a Node.js project:
Key Features:
- Package Management: Easily install, update, and manage packages using NPM.
- Dependencies: Automatically handle dependencies for your project.
- Scripts: Define and run custom scripts using npm run command.
- Versioning: Control package versions and easily update dependencies.
- Scopes: Organize packages under a specific scope to prevent naming conflicts.
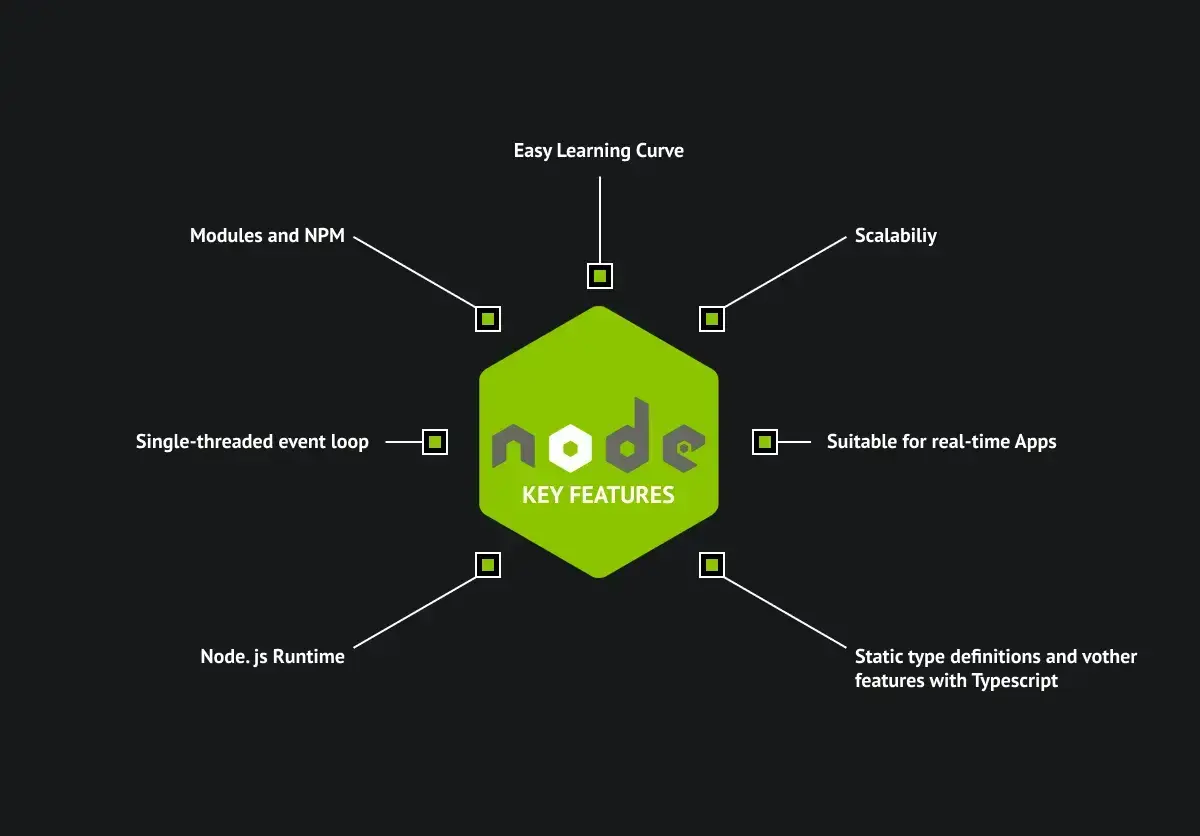
Who are the primary users of NPM?
NPM has a diverse range of primary users who benefit from its functionality and features. These users include:
- Developers: who leverage NPM to manage and share code libraries and packages.
- Project Managers: who rely on NPM to streamline project dependencies and ensure efficient development workflows.
- Organizations: that utilize NPM for scalable and collaborative software development.
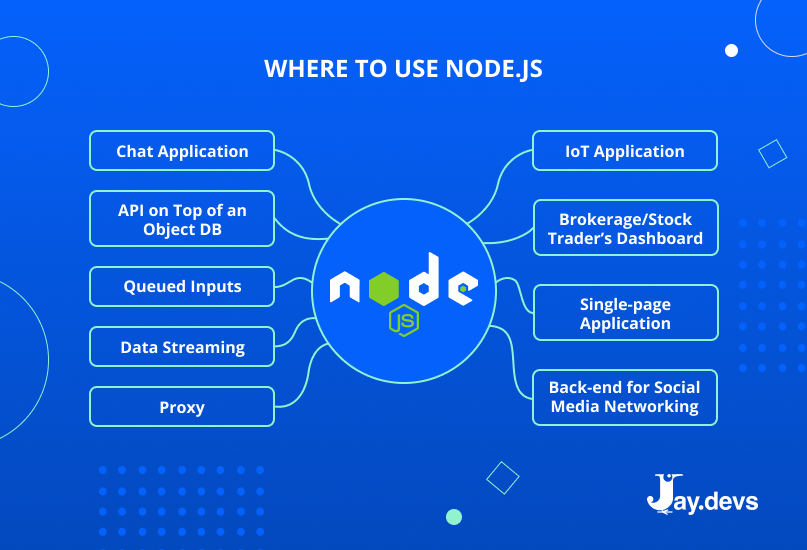
What are the typical use cases for NPM?
NPM (Node Package Manager) is primarily used for managing dependencies in Node.js projects. Some typical use cases for NPM include:
- Installing and managing packages
- Managing project dependencies
- Running scripts defined in the package.json file
- Version management and updating packages
How do you get started with NPM?
In order to get started with NPM, follow these steps:
- Install Node.js: First, make sure you have Node.js installed on your system. You can download and install it from the official Node.js website.
- Verify NPM installation: After installing Node.js, you can verify that NPM is installed by running
npm -vin your terminal. - Create a package.json file: You can create a
package.jsonfile for your project by runningnpm initin the project directory. - Install packages: Use the
npm installcommand to install packages for your project. - Manage versions: You can use NPM to manage dependencies and versions of packages in your project.

How does it work, in the context of NPM?
NPM, or Node Package Manager, is a package manager for JavaScript that helps in managing dependencies and libraries.
Key aspects of how NPM works:
- Package.json: Defines the project structure, dependencies, and scripts.
- npm install: Installs dependencies listed in package.json.
- npm update: Updates dependencies based on defined version ranges.
- npm init: Initializes a new NPM package with a package.json file.
Where can you deploy or implement NPM?
When using NPM, you can deploy or implement it in the following environments:
1. Local Development Environment:
NPM can be used in your local development environment for managing project dependencies and scripts.
2. Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) Pipeline:
You can integrate NPM into your CI/CD pipeline to automate the build, test, and deployment processes of your projects.
3. Cloud Services:
You can also utilize NPM in cloud services such as AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud Platform for deploying applications and managing dependencies in a scalable environment.
What are the limitations or challenges associated with NPM?
When working with NPM, there are several limitations and challenges that users may encounter:
- Security vulnerabilities: NPM packages can introduce security vulnerabilities to your project, especially if they contain malicious code or have not been updated to fix known vulnerabilities.
- Dependency conflicts: Managing dependencies in NPM can sometimes lead to conflicts between different packages that require conflicting versions of the same dependency.
- Performance issues: Installing many NPM packages and dependencies can impact the performance of your application, leading to longer build times and slower execution.

Comparisons of Other tools with NPM?
NPM, short for Node Package Manager, is a widely used tool for managing dependencies in Node.js projects. Below are some comparisons of NPM with other similar tools:
Yarn:
- Performance: Yarn is known for faster package installation compared to NPM.
- Offline Mode: Yarn provides better support for working offline.
- Deterministic: Yarn creates lock files, making dependency versions more deterministic.
Pnpm:
- Space Efficiency: Pnpm uses hard links and symlinks to save disk space.
- Speed: Pnpm claims to be faster than both Yarn and NPM due to its unique approach.
- Single Store: Pnpm stores dependencies in a single place on the disk.
